REVIEW
Reconstruction of skin friction topology in complex separated flows
Tianshu LiuAdv Aerodyn (2023) 5:28
https://doi.org/10.1186/s42774-023-00157-x
Quick Overview
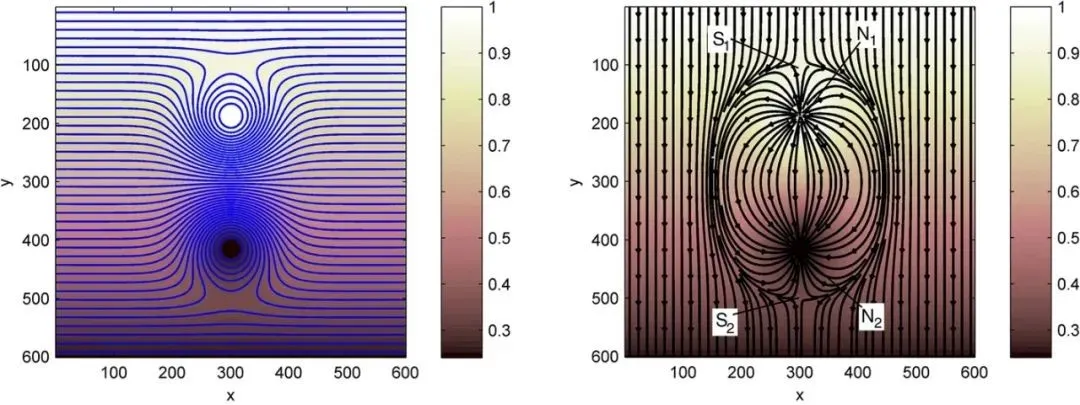
This paper presents a method for reconstructing skin friction topology in complex separated flows using surface pressure data. The method involves a variational approach and can accurately capture topological features such as critical points and separation lines. It has been successfully applied to shock-wave/boundary-layer interactions in wind tunnel experiments.

RESEARCH
Adaptive wave-particle decomposition in UGKWP method for high-speed flow simulations
针对高速流动的统一气体动理学自适应波-粒子方法
Yufeng Wei, Junzhe Cao, Xing Ji and Kun XuAdv Aerodyn (2023) 5:25
https://doi.org/10.1186/s42774-023-00156-y
Quick Overview
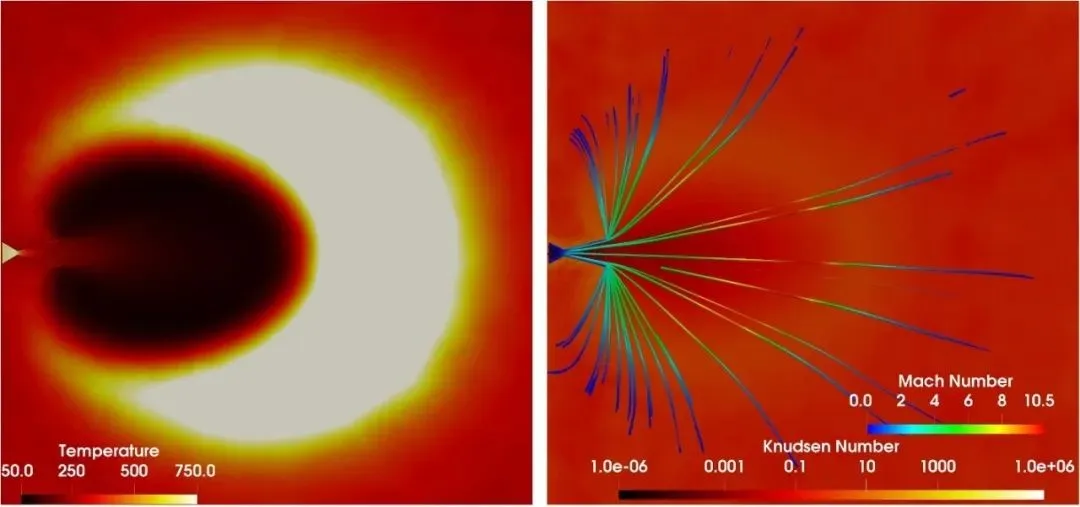
The UGKWP method has been developed for multiscale flow simulations using wave-particle decomposition. An adaptive version, AUGKWP, has been introduced to improve efficiency by considering both cell and gradient Knudsen numbers. It has been validated through various numerical tests and shows advantages in memory reduction and computational efficiency.
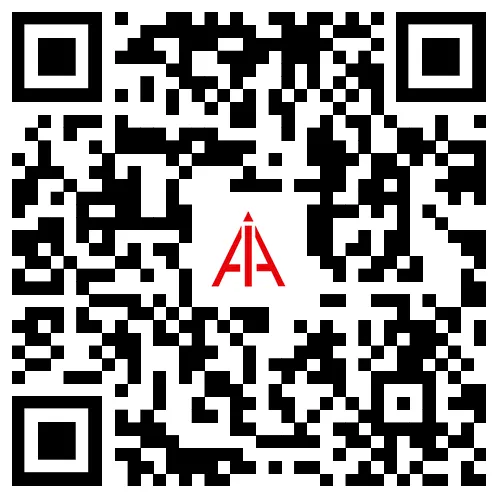

Effects of non-stationary wind velocity models on buffeting performance of closed-box girder suspension bridges
非平稳风速模型对闭口箱梁悬索桥的抖振性能影响分析
Rui Zhou, Yinan Lin, Peng Lu, Yongxin Yang and Jinbo ZhuAdv Aerodyn (2023) 5:26
https://doi.org/10.1186/s42774-023-00158-w
Quick Overview
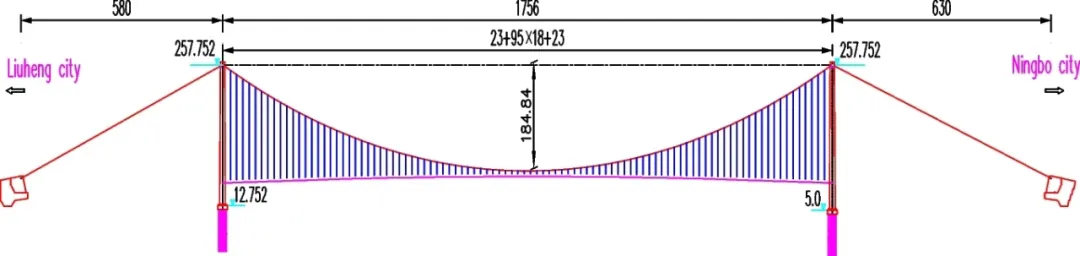
This research paper investigates the effects of non-stationary wind velocity models on the buffeting performance of long-span suspension bridges. Four non-stationary wind velocity models were established and compared, showing that turbulence intensities are larger with non-uniform modulation functions and decrease with a decrease in β.

Highly rarefied gas flows in rough channels of finite length高度稀薄气体在有限长度粗糙通道的流动Zheng Shi, Yulong Zhao, Wei Su and Lei WuAdv Aerodyn (2023) 5:27
https://doi.org/10.1186/s42774-023-00159-9
Quick Overview
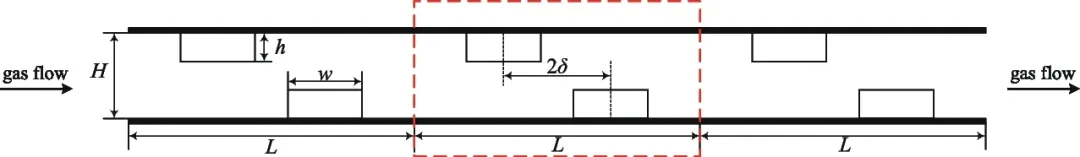
This research investigates the impact of surface bumps and channel length on rarefied gas flow in rough channels. It is found that small bumps can significantly reduce gas permeability, and the end effect is related to the channel's aspect ratio. The findings can explain the observed flow enhancement in graphene channels.

Hypersonic aerodynamic force balance using temperature compensated semiconductor strain gaugesHuacheng Qiu, Yanguang Yang, Peng Sun, Genming Chao, Yousheng Wu and Yingdong ChenAdv Aerodyn (2023) 5:29
https://doi.org/10.1186/s42774-023-00160-2
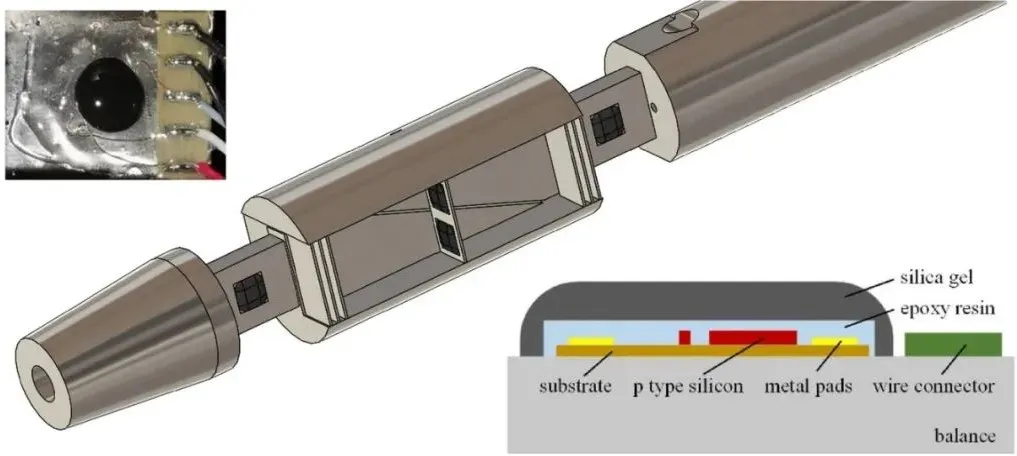
Quick Overview
A new three-component balance using temperature compensated semiconductor strain gauges has been designed, calibrated, and tested in a hypersonic low density wind tunnel. It has shown better strain resolution and accuracy compared to traditional metal foil strain gauges, with a static accuracy of 0.3% FS and dynamic accuracy established in a Mach 12 hypersonic flow. The balance has good experimental repeatability and has been validated through comparison with computational fluid dynamics simulations and reference wind tunnel results.

Experimental design for a novel co-flow jet airfoilHao Jiang, Weigang Yao and Min XuAdv Aerodyn (2023) 5:30
https://doi.org/10.1186/s42774-023-00161-1
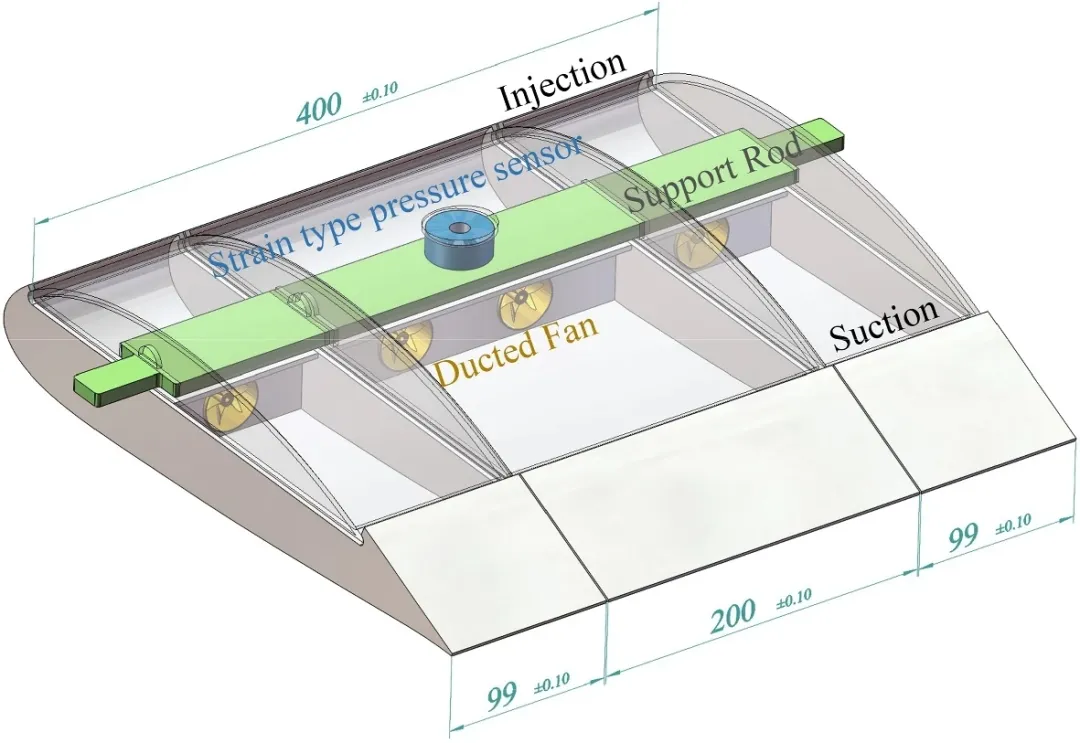
Quick Overview
This research paper discusses the design and validation of a novel co-flow jet airfoil through low-speed wind tunnel experiments. The airfoil has a tri-sectional design with a support rod for structural integrity and direct measurement of aerodynamic forces. Results show strong agreement with numerical simulations, demonstrating the effectiveness of the experimental framework.
