

Phenomics期刊2024年第三期封面图
01
A Novel Integrated Pipeline for Site-Specific Quantification of N-glycosylations
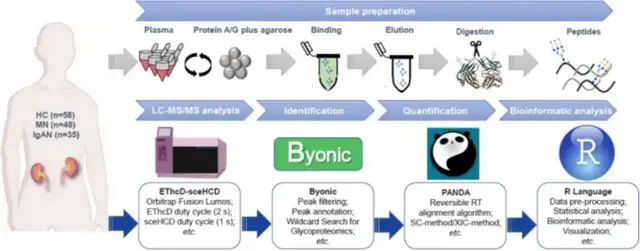
文章概览

扫二维码|查看原文
引用格式:
Zhao, Y., Zhang, Y., Meng, B. et al. A Novel Integrated Pipeline for Site-Specific Quantification of N-glycosylation. Phenomics 4, 213–226 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43657-023-00150-w
人类血浆免疫球蛋白γ分子(IgGs)的位点特异性n -糖基化变化已被证明可以调节免疫反应,并可作为准确诊断各种疾病的潜在生物标志物。然而,在大规模临床样本中准确定量完整的n -糖肽仍然是一个挑战,慢性肾脏疾病(CKDs)患者血浆IgG的定量n -糖基化尚未得到研究。在这项研究中,提出了一种新的集成完整的n -糖肽定量方法(称为GlycoQuant),它结合了该研究团队最近开发的质谱破碎法(EThcD-sceHCD)和完整的n -糖肽批量定量软件工具(升级版PANDA v.1.2.5)。实现了在一小时内纯化并消化了58名健康对照(HC)、48名膜性肾病(MN)患者和35名IgA肾病(IgAN)患者的血浆IgG。然后,使用EThcD-sceHCD-MS/MS对未富集的消化肽进行分析,提供了更高的光谱质量和更大的识别深度。使用升级版PANDA,对IgG进行了位点特异性n -糖基化定量。几种定量的完整n -糖肽不仅可以区分CKD和HC,还可以区分不同类型的CKD (MN和IgAN),并可能作为肾小管功能的准确诊断工具。此外,通过重新分析之前鉴定的细胞、尿液、血浆和组织样本中的完整n -糖肽,证明了该方法对复杂样品的适用性。这个方法可以应用于大规模的临床n -糖蛋白组学研究,促进新的糖基化生物标志物的发现。
Abstract
The site-specific N-glycosylation changes of human plasma immunoglobulin gamma molecules (IgGs) have been shown to modulate the immune response and could serve as potential biomarkers for the accurate diagnosis of various diseases. However, quantifying intact N-glycopeptides accurately in large-scale clinical samples remains a challenge, and the quantitative N-glycosylation of plasma IgGs in patients with chronic kidney diseases (CKDs) has not yet been studied. In this study, we present a novel integrated intact N-glycopeptide quantitative pipeline (termed GlycoQuant), which combines our recently developed mass spectrometry fragmentation method (EThcD-sceHCD) and an intact N-glycopeptide batch quantification software tool (the upgraded PANDA v.1.2.5). We purified and digested human plasma IgGs from 58 healthy controls (HCs), 48 patients with membranous nephropathy (MN), and 35 patients with IgA nephropathy (IgAN) within an hour. Then, we analyzed the digested peptides without enrichment using EThcD-sceHCD-MS/MS, which provided higher spectral quality and greater identified depth. Using upgraded PANDA, we performed site-specific N-glycosylation quantification of IgGs. Several quantified intact N-glycopeptides not only distinguished CKDs from HCs, but also different types of CKD (MN and IgAN) and may serve as accurate diagnostic tools for renal tubular function. In addition, we proved the applicability of this pipeline to complex samples by reanalyzing the intact N-glycopeptides from cell, urine, plasma, and tissue samples that we had previously identified. We believe that this pipeline can be applied to large-scale clinical N-glycoproteomic studies, facilitating the discovery of novel glycosylated biomarkers.
02
Identification of Key Factors in Cartilage Tissue During the Progression of Osteoarthritis Using a Non-targeted Metabolomics Strategy
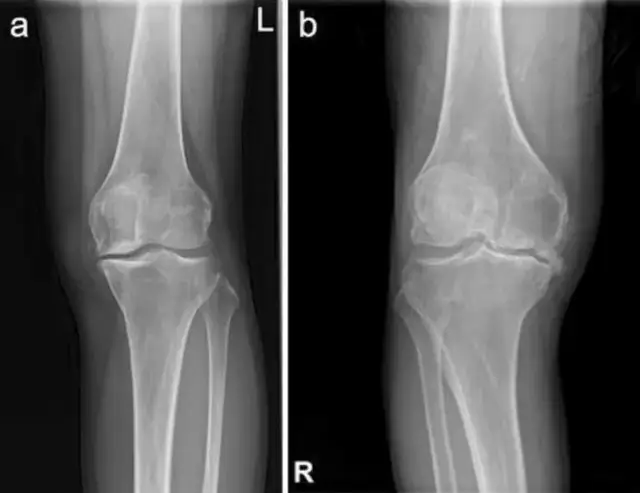
膝关节x线平片,左图为KL 3a级,右图为KL 4a级

扫二维码|查看原文
引用格式:
Sun, S., Chen, M., Zhang, T. et al. Identification of Key Factors in Cartilage Tissue During the Progression of Osteoarthritis Using a Non-targeted Metabolomics Strategy. Phenomics 4, 227–233 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43657-023-00123-z
该研究旨在利用非靶向代谢组学揭示骨关节炎(OA)进展的关键因素,并为OA患者寻找靶向治疗方法。22例计划行全膝关节置换术的膝关节OA患者根据膝关节X线平片分为Kellgren-Lawrence (KL) 3级(n = 16)和4级(n = 6)两组。术后对股骨软骨进行非靶向代谢组学分析。与3级患者相比,胆碱、2-丙基哌啶、鼠李糖和单甲基戊二酸的水平更高;4级患者的1-甲基组胺、鞘磷脂(SM) (d18:1/14:0)、零醇、3-(4-羟基苯基)-1-丙醇、5-氨基戊酰胺、二氢尿嘧啶、2-羟吡啶和3-氨基-2-哌酮较低。此外,两组的某些代谢途径存在显著差异,如泛酸和辅酶A (CoA)生物合成途径、甘油磷脂代谢途径、组氨酸代谢途径、赖氨酸降解途径、甘氨酸、丝氨酸和苏氨酸代谢途径、果糖和甘露糖代谢途径、嘧啶代谢途径和β -丙氨酸代谢途径。该工作采用非靶向代谢组学方法,筛选出差异代谢物和代谢途径,为进一步研究OA进展中的特异性标志物及其特异性途径提供了可靠的理论依据。
Abstract
This research was to reveal the key factors in the progression of osteoarthritis (OA) using non-targeted metabolomics and to find targeted therapies for patients with OA. Twenty-two patients with knee OA scheduled for total knee arthroplasty were divided into two groups: Kellgren–Lawrence (KL) grade 3 (n = 16) and grade 4 (n = 6), according to plain X-rays of the knee. After the operation, the cartilages of femur samples were analyzed using non-targeted metabolomics. When compared with grade 3 patients, the levels of choline, 2-propylpiperidine, rhamnose, and monomethyl glutaric acid were higher; while 1-methylhistamine, sphingomyelin (SM) (d18:1/14:0), zeranol, 3- (4-hydroxyphenyl)-1-propanol, 5-aminopentanamide, dihydrouracil, 2-hydroxypyridine, and 3-amino-2-piperidone were lower in grade 4 patients. Furthermore, some metabolic pathways were found to be significantly different in two groups such as the pantothenate and coenzyme A (CoA) biosynthesis pathway, the glycerophospholipid metabolism pathway, histidine metabolism pathway, lysine degradation pathway, glycine, serine and threonine metabolism pathway, fructose and mannose metabolism pathway, the pyrimidine metabolism pathway, and beta-alanine metabolism pathway. This work used non-targeted metabolomics and screened out differential metabolites and metabolic pathways, providing a reliable theoretical basis for further study of specific markers and their specific pathways in the progression of OA.
03
A Multimodal Approach for Detection and Assessment of Depression Using Text, Audio and Video
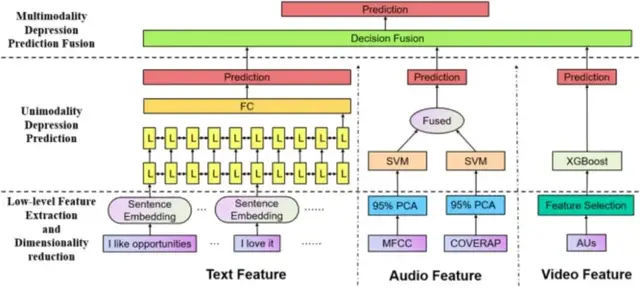
基于多模态输入特征的网络框图

扫二维码|查看原文
引用格式:
Zhang, W., Mao, K. & Chen, J. A Multimodal Approach for Detection and Assessment of Depression Using Text, Audio and Video. Phenomics 4, 234–249 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43657-023-00152-8
抑郁症是最常见的精神障碍之一,抑郁症的发病率每年都在增加。传统的诊断方法主要基于专业判断,容易产生个体偏差。因此,设计一种有效、稳健的抑郁症自动诊断方法至关重要。目前的人工智能方法在从长句子中提取特征的能力上是有限的。此外,当前的模型在大输入维数下的鲁棒性不强。为了解决这些问题,研究人员开发了一个由文本、音频和视频组成的多模态融合模型,用于抑郁症检测和评估任务。在文本模态中,利用预训练的句子嵌入提取语义表征,结合双向长短期记忆(BiLSTM)进行抑郁预测。本研究还利用主成分分析(PCA)对输入特征空间进行降维,并利用支持向量机(SVM)对音频模态进行抑郁预测。在视频模式中,使用极限梯度增强(XGBoost)进行特征选择和凹陷检测。最后用集合投票算法对不同模态的输出进行预测。在窘迫分析访谈语料wizard-of-Oz (DAIC-WOZ)数据集上的实验表明,该方法的性能有了很大的提高,加权F1得分为0.85,均方根误差(RMSE)为5.57,平均绝对误差(MAE)为4.48。该文提出的模型在抑郁检测和评估任务中都优于基线,并且被证明比其他现有的最先进的抑郁检测方法表现更好。
Abstract
Depression is one of the most common mental disorders, and rates of depression in individuals increase each year. Traditional diagnostic methods are primarily based on professional judgment, which is prone to individual bias. Therefore, it is crucial to design an effective and robust diagnostic method for automated depression detection. Current artificial intelligence approaches are limited in their abilities to extract features from long sentences. In addition, current models are not as robust with large input dimensions. To solve these concerns, a multimodal fusion model comprised of text, audio, and video for both depression detection and assessment tasks was developed. In the text modality, pre-trained sentence embedding was utilized to extract semantic representation along with Bidirectional long short-term memory (BiLSTM) to predict depression. This study also used Principal component analysis (PCA) to reduce the dimensionality of the input feature space and Support vector machine (SVM) to predict depression based on audio modality. In the video modality, Extreme gradient boosting (XGBoost) was employed to conduct both feature selection and depression detection. The final predictions were given by outputs of the different modalities with an ensemble voting algorithm. Experiments on the Distress analysis interview corpus wizard-of-Oz (DAIC-WOZ) dataset showed a great improvement of performance, with a weighted F1 score of 0.85, a Root mean square error (RMSE) of 5.57, and a Mean absolute error (MAE) of 4.48. Our proposed model outperforms the baseline in both depression detection and assessment tasks, and was shown to perform better than other existing state-of-the-art depression detection methods.
04
Kidney Function and Cardiovascular Disease: Evidence from Observational Studies and Mendelian Randomization Analyses

扫二维码|查看原文
引用格式:
Yang, W., Wu, X., Zhao, M. et al. Kidney Function and Cardiovascular Disease: Evidence from Observational Studies and Mendelian Randomization Analyses. Phenomics 4, 250–253 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43657-023-00145-7
既往观察性证据表明,肾功能不全与心血管疾病(CVD)风险增加相关,但其因果关系尚需深入探讨。本研究旨在基于大型人群研究评估多种肾功能指标与CVD及其主要亚型之间的关联,并通过孟德尔随机化(MR)方法评估潜在因果关系。研究使用了来自英国生物银行的306,246例个体水平数据,以及来自FinnGen、CARDIoGRAMplusC4D及MEGASTROKE等大型研究的基因组数据分析结果。纳入分析的肾功能指标包括血液中胱抑素C和肌酐水平、尿白蛋白与肌酐比值(uACR)以及基于三种方法估算的肾小球滤过率(eGFR)。研究结果显示,在基于个体水平数据的观察性分析中,肾功能指标降低与CVD风险增加显著相关。其中,基于胱抑素C和肌酐计算的eGFR每降低一个标准差,CVD风险增加11%(风险比=0.89;95%置信区间:0.87-0.90)。然而,双样本MR分析未发现肾功能指标与CVD及其亚型风险之间具有显著关联。本研究表明,尽管观察性分析发现肾功能指标与CVD风险的负相关性,但这一关联未在大规模MR分析中得到支持,尚需要进一步探讨两者关联的潜在生物学机制。
Abstract
Observational studies have identified that declined kidney function was associated with a higher risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD). However, the causation of such associations requires further exploration. Here, we compared the observational associations of various kidney function measurements with CVD and its major subtypes and further assessed the potential causality using Mendelian randomization (MR) analyses with individual-level data of 306,246 participants from the UK Biobank and genome-wide association study summary-level data from FinnGen consortium, Coronary ARtery DIsease Genome wide Replication and Meta-analysis plus The Coronary Artery Disease Genetics (CARDIoGRAMplusC4D) consortium, and MEGASTROKE Consortium, respectively. Kidney function measurements included circulating levels of cystatin C and creatinine, urine albumin-to-creatinine ratio (uACR), and estimated glomerular filtration rates (eGFR) from three chronic kidney disease epidemiology collaboration formulae (i.e., that using cystatin C, creatinine, and both). In the observational analyses, decreased kidney function measurements were associated with a higher risk of CVD in the UK Biobank study. For example, per one standard deviation decrease in baseline estimated glomerular filtration rates using both cystatin C and creatinine (eGFRcys + cre) was associated with 11% higher risk of CVD (hazard ratio = 0.89; 95% confidence interval, 0.87–0.90). In contrast, two-sample MR analyses did not suggest significant associations of any genetically instrumented kidney function measurement with the risk of CVD or its subtypes. Our findings suggested the inverse associations of kidney function measurements with CVD risk from observational studies were not supported by large MR analyses.
05
Report on the 4th Board Meeting of the International Human Phenome Consortium.

扫二维码|查看原文
引用格式:
Tian, M., Liu, H., Peng, S. et al. Report on the 4th Board Meeting of the International Human Phenome Consortium. Phenomics 4, 254–256 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43657-023-00139-5
表型组是生物医学下一个创新来源已成为共识。国际人类表型组研究协作组(IHPC)理事会致力于大规模人类表型组研究工作和促进人类表型组计划全球网络协作,在指导国际人类表型组计划的战略、实施以及协调IHPC成员等方面发挥着重要作用。第四届国际人类表型组研究协作组理事会会议于2022年12月13日举行。会议期间,多个主题演讲介绍了表型组学的最新进展。全球首个人类表型组“导航图”成功构建,并在肢体发育、疾病预防和早期诊断方面有诸多发现,显示出巨大的潜力。结合基因组-表型组测序、大数据分析和健康指导为增强个人健康提供了新方案。从健康、疾病到康复状态的表型组学轨迹为了解与COVID-19相关的代谢风险提供了洞见。来自加纳、马来西亚、印度和俄罗斯的理事会成员介绍了各自的研究计划和科研进展。IHPC理事会审议了《人类表型组测量指南》和《共建全球人类表型组数据库(PhenoBank)倡议》。会议还介绍了IHPC会刊《表型组学(英文)》(Phenomics)期刊的年度报告。本次理事会就实验室协调、可互操作的数据库和标准化平台进行了富有成效的讨论,将助力国际人类表型组计划的协同研究。
Abstract
Phenome has become a consensus as the next innovation source of biomedicine. As the global network dedicated to large-scale research efforts on human phenome and promoting the Human Phenome Project, the Board of International Human Phenome Consortium (IHPC) plays an essential role to guide the strategy and implementation of international human phenome project and to ensure coordination across the IHPC members. The 4th International Human Phenome Consortium Board Meeting was held virtually on December 13, 2022. During the meeting, the keynote speeches highlighted the latest advancements in phenomics. The construction and discoveries of the first human phenome Atlas had shown promising potential in limb development, disease prevention, and early diagnosis. Combining genome-phenome sequencing, analysis, and wellness coaching enhanced individual wellness. Phenomics trajectories from healthy to diseased states and recovery provided insight into the metabolic risk spaces associated with COVID-19. Board members from Ghana, Malaysia, India, and Russia presented their own plans and research progress. The IHPC Board deliberated on the “Framework Guidelines for Human Phenome-related Measurements” and “Proposal of the PhenoBank Initiative”. The meeting also featured a presentation of the annual report of the IHPC Journal Phenomics. Laboratory coordination, interoperable databases, and standardized platforms were productively discussed, which would enable concerted research efforts of the Human Phenome Project.
06
Investigation on Phenomics of Traditional Chinese Medicine from the Diabetes

糖尿病中医诊疗体系——“分型、分期、辨证策略”

扫二维码|查看原文
引用格式:
Zhang, B., Zhou, L., Chen, K. et al. Investigation on Phenomics of Traditional Chinese Medicine from the Diabetes. Phenomics 4, 257–268 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43657-023-00146-6
中医药具有上千年的应用历史,在预防各种慢性疾病方面具有独特的优势,近年来,中医药的发展呈现出机遇与挑战并存的局面。表型组学是生命科学研究的一个新兴领域,它与中医的认知视角有许多相似之处。因此,如何开展中医与表型组学的跨学科研究值得深入探讨。糖尿病是世界范围内最常见的慢性非传染性疾病之一,中医药在糖尿病治疗的各个阶段都发挥着重要作用,但其分子机制尚不清楚。表型组学研究不仅可以揭示中医隐藏的科学内涵,而且可以为中医与西医的融合与互补搭建桥梁。面对中医药表型组学研究面临的挑战,该文建议运用State-target theory (STT)对相关研究进行统筹规划,即关注各阶段疾病的发展、变化趋势和核心靶点,深化对中医疾病表型和草药治疗机制的认识。
Abstract
With thousands of years of application history, traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) has unique advantages in the prevention of various chronic diseases, and in recent years, the development of TCM has presented a situation where opportunities and challenges coexist. Phenomics is an emerging area of life science research, which has numerous similarities to the cognitive perspective of TCM. Thus, how to carry out the interdisciplinary research between TCM and phenomics deserves in-depth discussion. Diabetes is one of the most common chronic non-communicable diseases around the world, and TCM plays an important role in all stages of diabetes treatment, but the molecular mechanisms are difficult to elucidate. Phenomics research can not only reveal the hidden scientific connotations of TCM, but also provide a bridge for the confluence and complementary between TCM and Western medicine. Facing the challenges of the TCM phenomics research, we suggest applying the State-target theory (STT) to overall plan relevant researches, namely, focusing on the disease development, change trends, and core targets of each stage, and to deepen the understanding of TCM disease phenotypes and the therapeutic mechanisms of herbal medicine.
07
Expert Consensus on Big Data Collection of Skin and Appendage Disease Phenotypes in Chinese
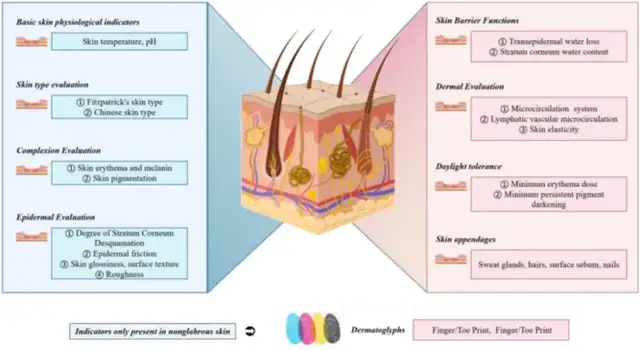
皮肤和附属物表型测量条目的系统分组

扫二维码|查看原文
引用格式:
Zhao, S., Luo, Z., Wang, Y. et al. Expert Consensus on Big Data Collection of Skin and Appendage Disease Phenotypes in Chinese. Phenomics 4, 269–292 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43657-023-00142-w
皮肤和附属物表型大数据的收集使个体特征的评估和异常的早期发现成为可能,从而彻底改变了个性化诊断和治疗领域。为建立标准化的表型大数据采集和测量体系,对测量条目进行了系统分类,并针对不同使用场景的需求,提出了测量条目、环境设备要求和采集流程的建议。还根据不同的索引特征推荐了具体的收集地点。一项多中心、多区域的合作已经启动,旨在收集中国人群健康和患病皮肤表型的大数据。这些数据将与患者疾病信息进行关联,探索影响皮肤表型的因素,分析可预测预后的表型数据特征,最终促进对皮肤病病理生理、发病机制及治疗途径的探索。非侵入性皮肤测量机器人也在开发中。该共识旨在为中国皮肤及附属物表型组学研究和表型测量标准化提供参考。
Abstract
The collection of big data on skin and appendage phenotypes has revolutionized the field of personalized diagnosis and treatment by enabling the evaluation of individual characteristics and early detection of abnormalities. To establish a standardized system for collecting and measuring big data on phenotypes, a systematic categorization of measurement entries has been undertaken, accompanied by recommendations on measurement entries, environmental equipment requirements, and collection processes, tailored to the needs of different usage scenarios. Specific collection sites have also been recommended based on different index characteristics. A multi-center, multi-regional collaboration has been initiated to collect big date on phenotypes of healthy and diseased skin in the Chinese population. This data will be correlated with patient disease information, exploring the factors influencing skin phenotype, analyzing the phenotypic data features that can predict prognosis, and ultimately promoting the exploration of the pathophysiology and pathogenesis of skin diseases and therapeutic approaches. Non-invasive skin measurement robots are also in development. This consensus aims to provide a reference for the study of phenomics and the standardization of phenotypic measurements of skin and appendages in China.
08
Gut Microbiota in Primary Osteoporosis: a Systematic Review
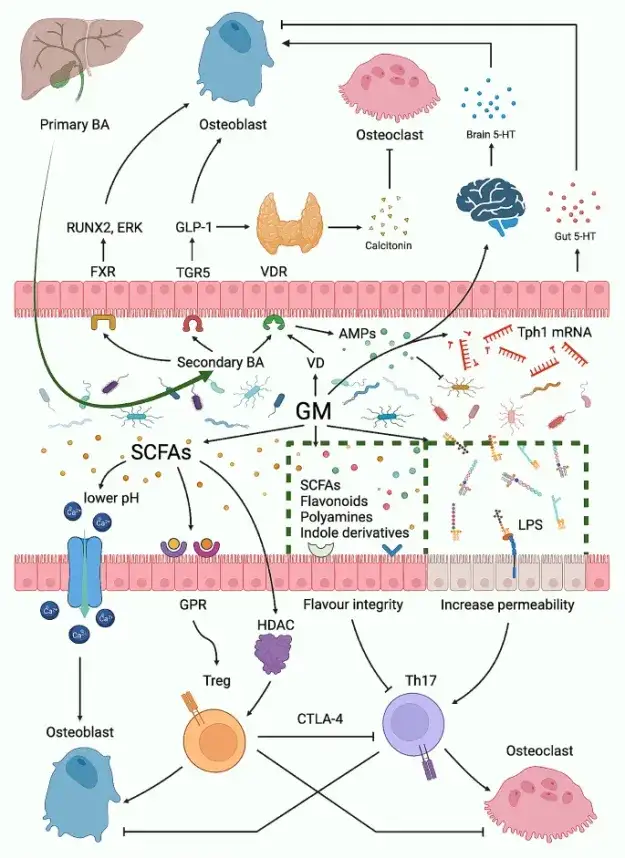
肠道菌群影响骨代谢的机制概览

扫二维码|查看原文
引用格式:
Ji, J., Cai, F., Yuan, C. et al. Gut Microbiota in Primary Osteoporosis: a Systematic Review. Phenomics 4, 293–297 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43657-024-00164-y
肠道微生物群(GM)与原发性骨质疏松症之间的联系已经引起了广泛的关注。在该研究中,研究者对采用高通量测序方法的10项研究进行了系统回顾。值得注意的是,在回顾的研究中,分类概况表现出明显的异质性。综合分析机制研究筛选出骨质疏松症预防和治疗的潜在靶点。该研究评估了以往研究的局限性,并提出了优化测序技术和实验设计的建议。建议基于多组学和扩展表型的更大规模纵向队列来全面表征GM在骨质疏松症发病机制中的作用。
Abstract
The link between gut microbiota (GM) and primary osteoporosis has garnered substantial attention. In this study, we conducted a systematic review encompassing 10 studies that employed high-throughput sequencing methodologies. Notably, the taxonomic profiles exhibited pronounced heterogeneity across reviewed studies. A combined analysis of mechanistical studies screened out potential targets for osteoporosis prevention and treatment. We appraised the limitations in previous studies, and proposed suggestions for optimizing sequencing techniques and experimental designs. Larger-size longitudinal cohorts based on multi-omics and extended phenotypes are recommended to comprehensively characterize the involvement of GM in the pathogenesis of osteoporosis.
09
Synergistically Augmenting Cancer Immunotherapy by Physical Manipulation of Pyroptosis Induction
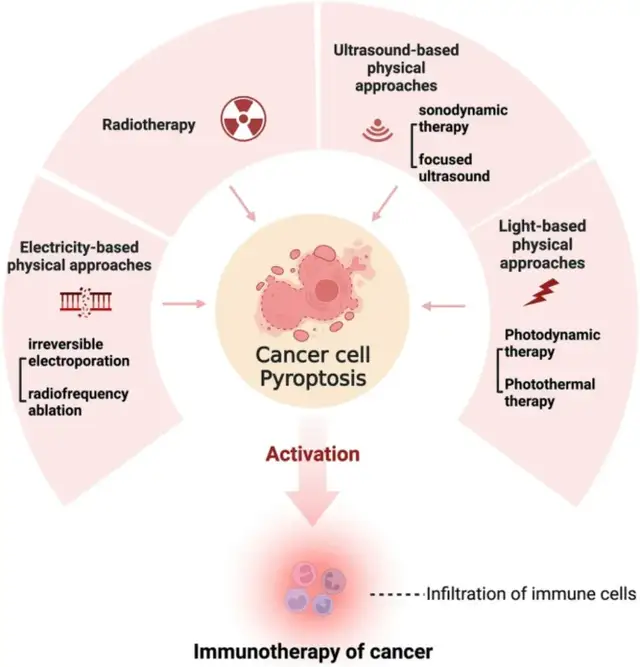
焦亡和物理方法在癌症治疗中的概述

扫二维码|查看原文
引用格式:
Zhao, C., Zheng, T., Wang, R. et al. Synergistically Augmenting Cancer Immunotherapy by Physical Manipulation of Pyroptosis Induction. Phenomics 4, 298–312 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s43657-023-00140-y
焦亡是一种新发现的程序性细胞死亡类型,由gasdermin家族和caspase介导。它的特点是炎症小体的形成和以下炎症反应。近年来的研究已经阐明了诱导焦亡在癌症治疗中的价值。焦亡过程中产生的炎性细胞因子可触发免疫反应抑制恶性肿瘤。癌症治疗的物理方法,包括放射治疗、基于光的技术(光动力和光热疗法)、基于超声的技术(声动力治疗和聚焦超声)和基于电的技术(不可逆电穿孔和射频消融),在临床应用中是有效的。最近的研究报道,焦亡参与治疗过程的物理途径。根据最近的研究,利用物理方法操纵焦亡可以用于对抗癌症。热触发免疫治疗可与原有的抗肿瘤方法相结合,实现协同治疗,提高治疗效果。研究还表明,增强焦亡可能会增加癌细胞对某些物理方法的敏感性。在此,该文进行了一个全面的文献综述,重点关注焦亡和各种物理方法之间的联系,为癌症及其潜在的机制。该文还讨论了热触发免疫疗法在物理手法治疗过程中的作用。
Abstract
Pyroptosis is a newly recognized type of programmed cell death mediated by the gasdermin family and caspase. It is characterized by the formation of inflammasomes and the following inflammatory responses. Recent studies have elucidated the value of pyroptosis induction in cancer treatment. The inflammatory cytokines produced during pyroptosis can trigger immune responses to suppress malignancy. Physical approaches for cancer treatment, including radiotherapy, light-based techniques (photodynamic and photothermal therapy), ultrasound-based techniques (sonodynamic therapy and focused ultrasound), and electricity-based techniques (irreversible electroporation and radiofrequency ablation), are effective in clinical application. Recent studies have reported that pyroptosis is involved in the treatment process of physical approaches. Manipulating pyroptosis using physical approaches can be utilized in combating cancer, according to recent studies. Pyroptosis-triggered immunotherapy can be combined with the original anti-tumor methods to achieve a synergistic therapy and improve the therapeutic effect. Studies have also revealed that enhancing pyroptosis may increase the sensitivity of cancer cells to some physical approaches. Herein, we present a comprehensive review of the literature focusing on the associations between pyroptosis and various physical approaches for cancer and its underlying mechanisms. We also discussed the role of pyroptosis-triggered immunotherapy in the treatment process of physical manipulation.