Volume 18 Issue 9

Cover illustration
Municipal water and wastewater treatment is essential to control pollution and protect water ecology. More importantly, it has become a key link in promoting sustainable development for society, the economy, and the environment.
Urban water treatment facilities have greatly improved the quality of life for city dwellers. These advanced systems ensure the purification and supply of clean water, making it safe for drinking, cooking, and daily use. As a result, the incidence of waterborne diseases has been reduced, improving public health. In addition, these plants help protect the environment by treating wastewater before discharging into rivers or lakes. This conserves our precious water resources and supports the ecological balance. In essence, the presence of efficient water treatment facilities in cities has led to a better, healthier, and more sustainable lifestyle for residents.
本期封面主题
市政供水和污水处理对于控制污染和保护水生态至关重要。更重要的是,它已成为推动社会、经济和环境可持续发展的重要环节。
城市水处理设施极大地提高了城市居民的生活质量。这些先进的系统确保了水的净化和清洁水的供应,使得饮用水、烹饪用水和日常用水安全。因此,水传播疾病的发生率降低,提高了公共卫生水平。此外,这些设施通过在排放到河流或湖泊之前处理废水,帮助保护环境,保护了我们的宝贵水资源,并保持生态平衡。本质上,城市中高效水处理设施的存在,为居民带来了更好、更健康、更可持续的生活方式。
Table of content
Review Article
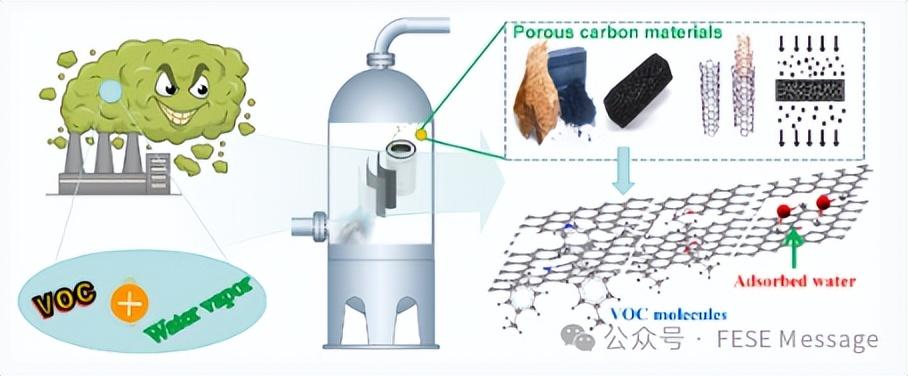
Enhancing comprehension of water vapor on adsorption performance of VOC on porous carbon materials and its application challenge
Front. Environ. Sci. Eng., 2024, 18(9): 110
https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-024-1870-x
Research Article
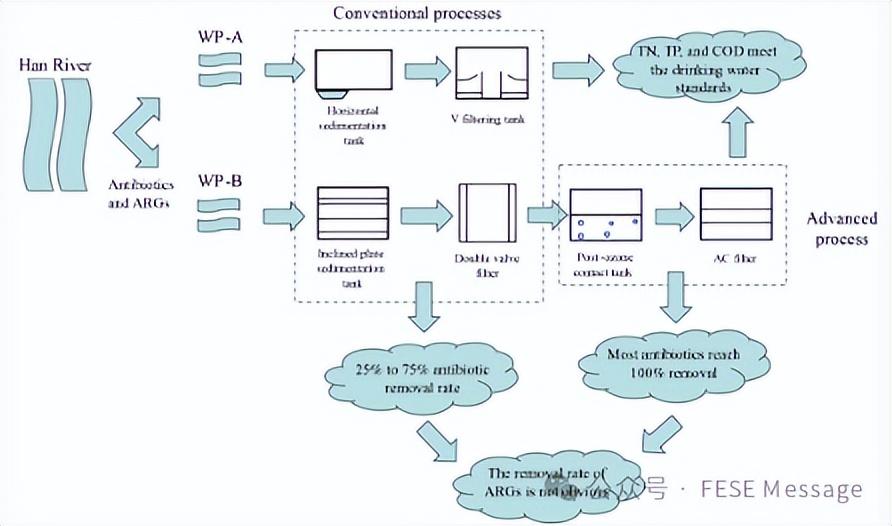
Distribution characteristics and removal rate of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes in different treatment processes of two drinking water plants
Front. Environ. Sci. Eng., 2024, 18(9): 117
https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-024-1877-3
Advanced modeling of the absorption enhancement of black carbon particles in chamber experiments by considering the morphology and coating thickness
Front. Environ. Sci. Eng., 2024, 18(9): 116
https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-024-1876-4

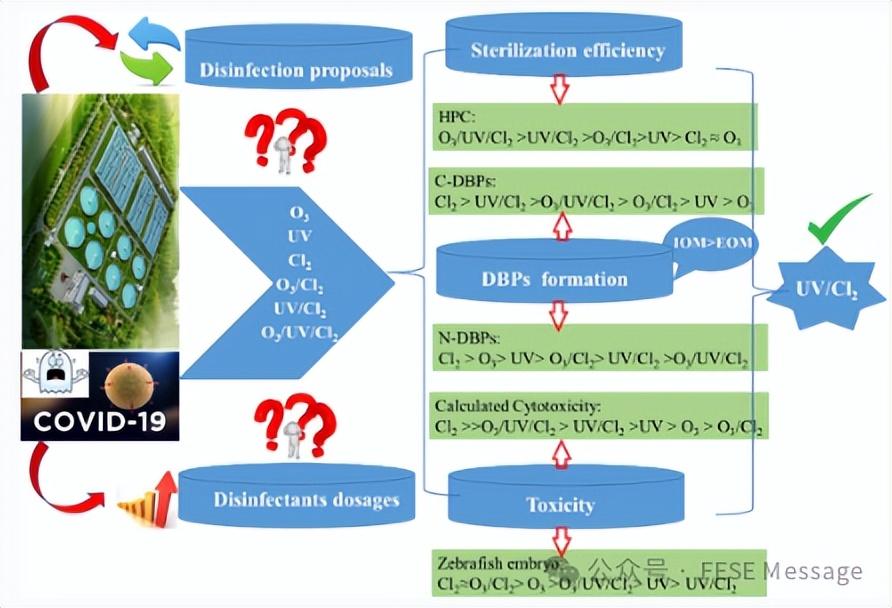
Alternate disinfection approaches or raise disinfectant dosages for sewage treatment plants to address the COVID-19 pandemic? From disinfection efficiency, DBP formation, and toxicity perspectives
Front. Environ. Sci. Eng., 2024, 18(9): 115
https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-024-1875-5
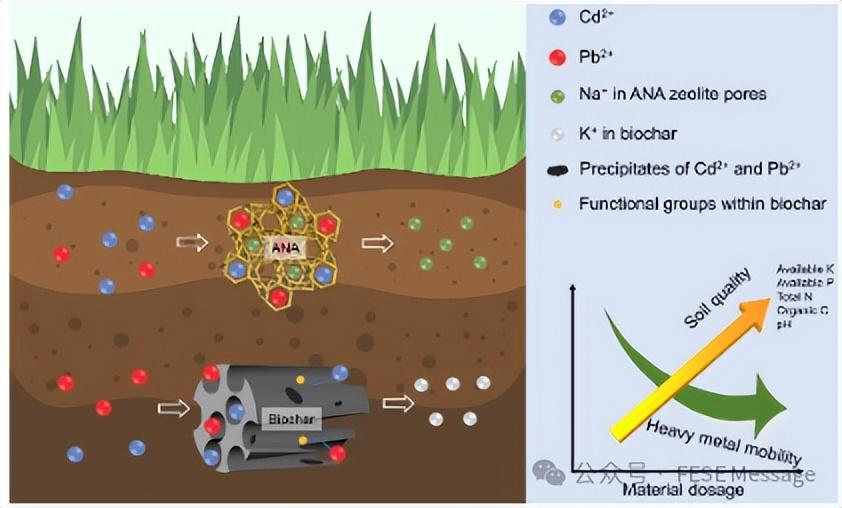
Mechanistic insights into the synergetic remediation and amendment effects of zeolite/biochar composite on heavy metal-polluted red soil
Front. Environ. Sci. Eng., 2024, 18(9): 114
https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-024-1874-6
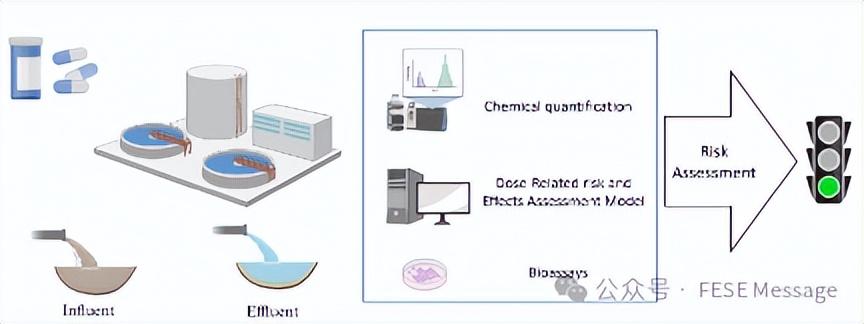
Use of DREAM to assess relative risks of presence of pharmaceuticals and personal care products from a wastewater treatment plant
Front. Environ. Sci. Eng., 2024, 18(9): 113
https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-024-1873-7
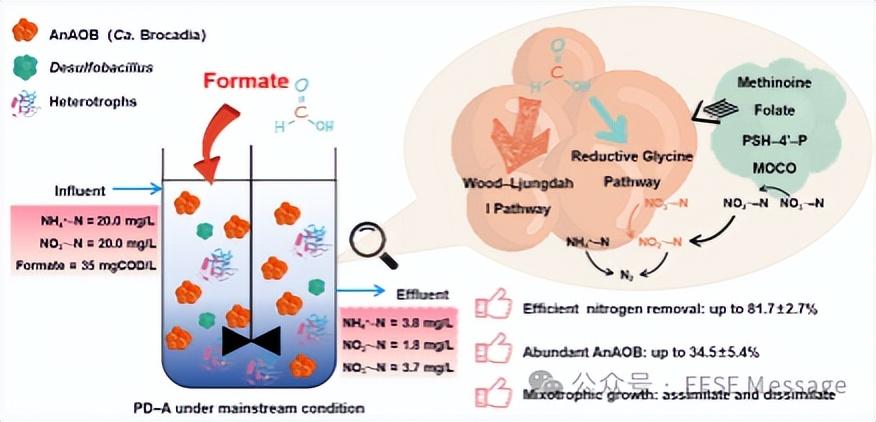
Unraveling the role of formate in improving nitrogen removal via coupled partial denitrification-anammox
Front. Environ. Sci. Eng., 2024, 18(9): 112
https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-024-1872-8
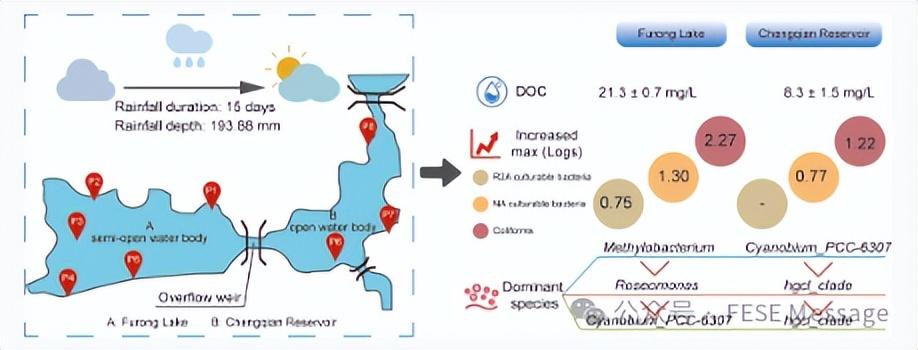
The variation of microbiological characteristics in surface waters during persistent precipitation
Front. Environ. Sci. Eng.,2024, 18(9): 111
https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-024-1871-9
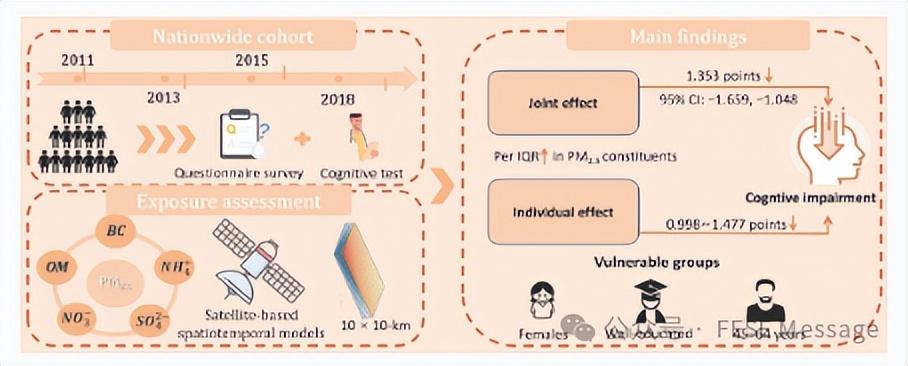
Cognitive impairment associated with individual and joint exposure to PM2.5 constituents in a Chinese national cohort
Front. Environ. Sci. Eng., 2024, 18(9): 109
https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-024-1869-3
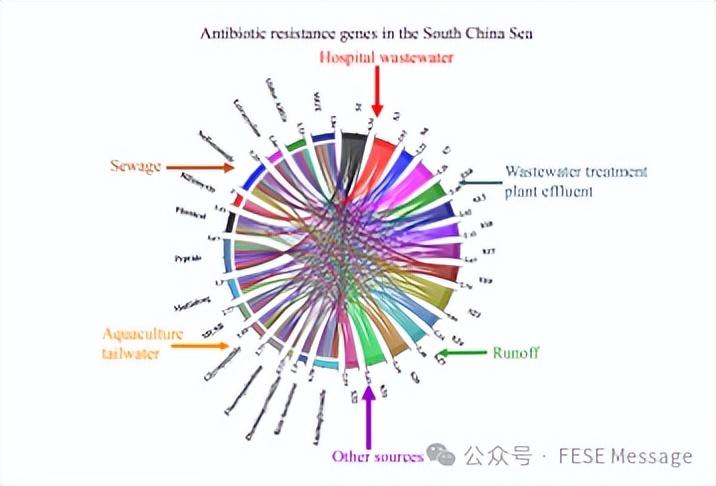
Occurrence and possible sources of antibiotic resistance genes in seawater of the South China Sea
Front. Environ. Sci. Eng., 2024, 18(9): 108
https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-024-1868-4
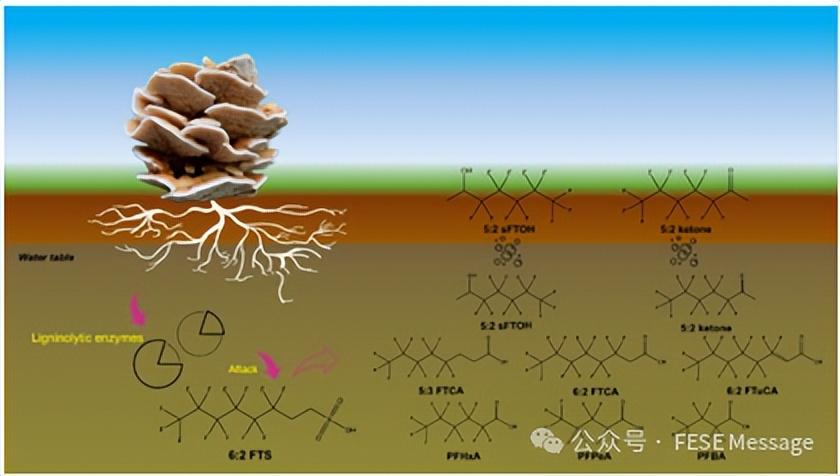
Biotransformation of 6:2 fluorotelomer sulfonate (6:2 FTS) in sulfur-rich media by Trametopsis cervina
Front. Environ. Sci. Eng., 2024, 18(9): 107
https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-024-1867-5
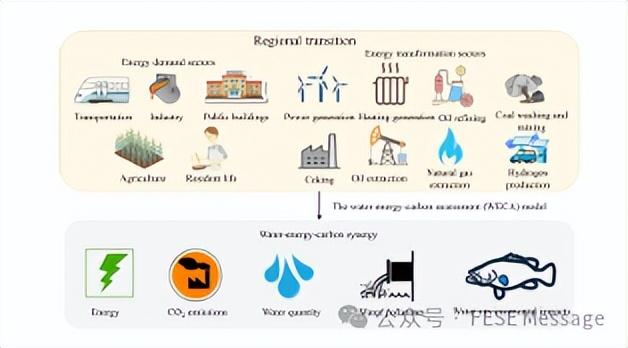
Synergetic pathways of water-energy-carbon in ecologically vulnerable regions aiming for carbon neutrality: a case study of Shaanxi, China
Front. Environ. Sci. Eng., 2024, 18(9): 106
https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-024-1866-6