A*算法是一种高效的路径搜索算法,结合了Dijkstra算法的准确性(确保最短路径)和贪心最佳优先搜索的高效性。它通过启发式函数(Heuristic Function)动态调整搜索方向,适用于网格地图、游戏导航等场景。
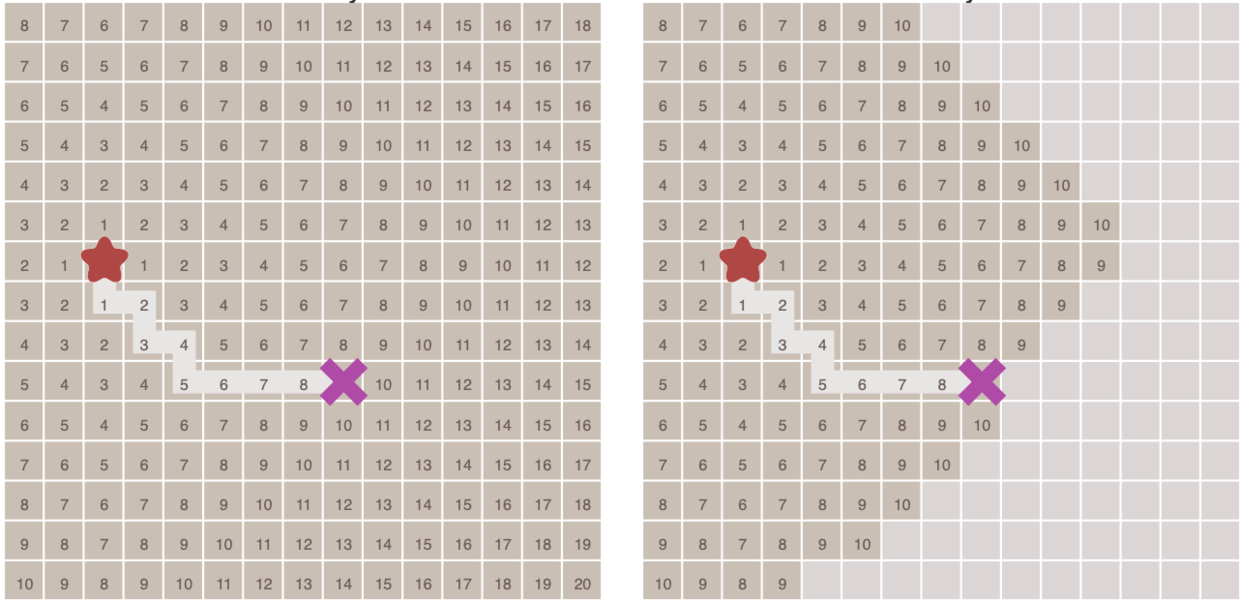
评估每个节点的优先级:[ f(n) = g(n) + h(n) ]- g(n):从起点到节点n的实际代价。
- h(n):从节点n到终点的预估代价(启发式函数,需可采纳,即不高估实际代价)。
算法步骤初始化两个列表:
开放列表(Open List):存储待探索节点(优先队列)。
关闭列表(Closed List):存储已探索节点。
将起点加入开放列表。
循环直到找到终点或开放列表为空:
取出开放列表中f值最小的节点作为当前节点。
若当前节点为终点,结束循环并回溯路径。
遍历当前节点的相邻节点:
跳过障碍物或关闭列表中的节点。
若相邻节点不在开放列表,计算其g、h、f值并加入。
若已在开放列表且新路径更优(g更小),更新父节点及g、f值。
路径生成:从终点回溯父节点至起点。
启发式函数选择曼哈顿距离(四方向移动):[ h(n) = |x_1 - x_2| + |y_1 - y_2| ]
对角距离(八方向移动):[ h(n) = (|x_1 - x_2|, |y_1 - y_2|) ]
欧几里得距离(任意方向,通常不可采纳):[ h(n) = ]
Python代码实现import heapqclass Node: def __init__(self, parent=None, position=None): self.parent = parent self.position = position # (x,y) self.g = 0 # 实际代价 self.h = 0 # 启发式预估代价 self.f = 0 # f = g + h def __eq__(self, other): return self.position == other.position def __lt__(self, other): return self.f < other.fdef astar(maze, start, end): # 初始化起点和终点节点 start_node = Node(None, start) end_node = Node(None, end) open_list = [] closed_list = [] heapq.heappush(open_list, (start_node.f, start_node)) # 四方向移动(上、下、左、右) directions = [(0, 1), (0, -1), (-1, 0), (1, 0)] while open_list: current_f, current_node = heapq.heappop(open_list) closed_list.append(current_node) # 找到终点,回溯路径 if current_node == end_node: path = [] while current_node: path.append(current_node.position) current_node = current_node.parent return path[::-1] # 反转路径 # 遍历相邻节点 children = [] for dx, dy in directions: x = current_node.position[0] + dx y = current_node.position[1] + dy if not (0 <= x < len(maze) and 0 <= y < len(maze[0])): continue # 超出地图范围 if maze[x][y] == 1: continue # 障碍物 new_node = Node(current_node, (x, y)) children.append(new_node) for child in children: # 跳过已探索节点 if any(child == closed_child for closed_child in closed_list): continue # 计算g、h、f值 child.g = current_node.g + 1 child.h = abs(child.position[0] - end_node.position[0]) + \ abs(child.position[1] - end_node.position[1]) # 曼哈顿距离 child.f = child.g + child.h # 若节点已在开放列表且代价更高,跳过 if any(child.position == open_node.position and child.g >= open_node.g for (_, open_node) in open_list): continue heapq.heappush(open_list, (child.f, child)) return None # 路径不存在# 示例地图(0可通过,1为障碍)maze = [ [0, 0, 0, 0, 0], [0, 1, 1, 1, 0], [0, 0, 0, 0, 0], [1, 1, 1, 0, 1], [0, 0, 0, 0, 0]]start = (0, 0)end = (4, 4)path = astar(maze, start, end)print("路径坐标:", path)
示例输出路径坐标: [(0, 0), (0, 1), (0, 2), (1, 2), (2, 2), (2, 3), (3, 3), (4, 3), (4, 4)]
算法分析优点:确保找到最短路径(启发式函数可采纳时),效率高于BFS和Dijkstra。
缺点:开放列表维护成本高,大地图可能消耗较多内存。
优化方向:二叉堆优化开放列表,跳点搜索(JPS)减少节点扩展。
通过灵活调整启发式函数,A*可适应不同场景需求,是路径规划领域的经典算法。
