

▸Cancer Innovation《肿瘤学创新(英文)》是由教育部主管,清华大学主办,清华大学出版社与 Wiley战略合作下出版的一本跨学科的开放获取(OA)英文期刊。
▸Cancer Innovation是一本聚焦于肿瘤医学前沿的英文期刊,致力于促进医学与工学、信息学、药学、生物学等多学科交叉,引导肿瘤专业与心血管、呼吸、神经、生殖等跨专业融合。
▸Cancer Innovation已入选“2022年中国科技期刊卓越行动计划高起点新刊项目”,已被国际知名数据库ESCI、PMC、Scopus、DOAJ、CAS(美国化学文摘)收录。
▸Cancer Innovation名誉主编由中国工程院院士、国家癌症中心/中国医学科学院肿瘤医院国家新药(抗肿瘤)临床研究中心主任徐兵河院士,中国工程院院士、北京大学国际癌症研究院院长、北京大学健康医疗大数据国家研究院院长詹启敏院士,以及中国工程院院士、中科院上海药物研究所丁健院士共同担任,主编由国家癌症中心/中国医学科学院肿瘤医院马飞教授担任。
▸期刊发表论文类型多元,包括Original Article, Review, Clinical Guideline, Technical Report, Case Report, Commentary, News, Study Protocol, Meta-Analysis, Letter与Editorial。
▸2025年前免收版面费。

第3卷第6期(2024.12)
注:本文中*表示通讯作者。
REVIEW
01
标题
TRIP13: A promising cancer immunotherapy target
TRIP13:一个有前途的癌症免疫治疗靶点
作者
Shengnan Jing, Liya Zhao, Liwen Zhao, Yong-Jing Gao*, Tianzhen He*
图片摘要
(点击图片即可免费阅读、下载全文)
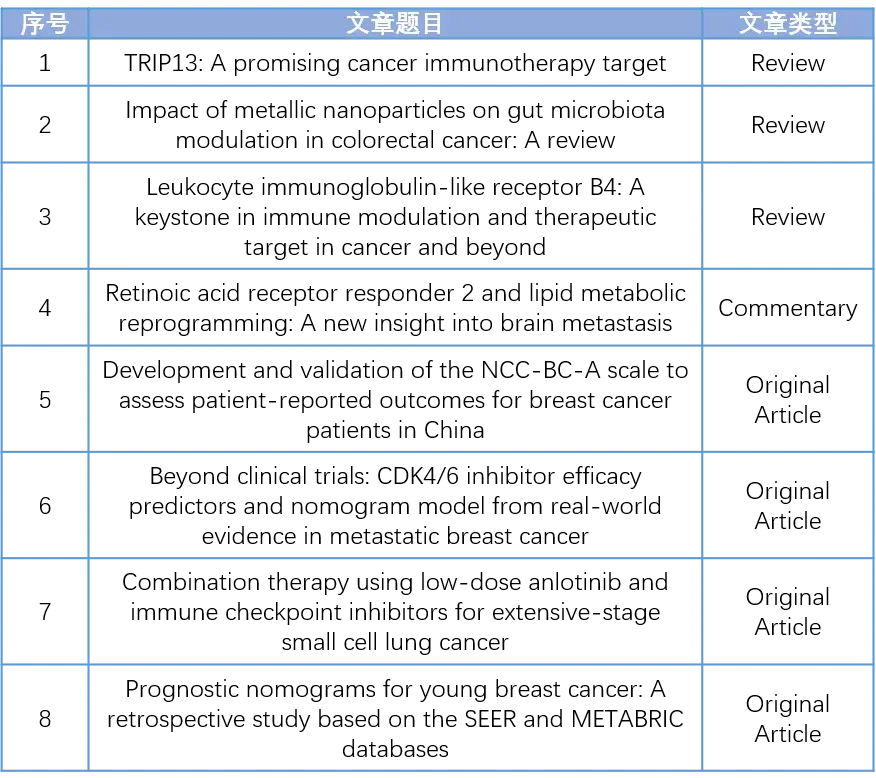
The tumor microenvironment (TME) facilitates tumor development through intricate intercellular signaling, thereby supporting tumor growth and suppressing the immune response. Thyroid hormone receptor interactor 13 (TRIP13), an AAA+ ATPase, modulates the conformation of client macromolecules, consequently influencing cellular signaling pathways. TRIP13 has been implicated in processes such as proliferation, invasion, migration, and metastasis during tumor progression. Recent studies have revealed that TRIP13 also plays a role in immune response suppression within the TME. Thus, inhibiting these functions of TRIP13 could potentially enhance immune responses and improve the efficacy of immune checkpoint inhibition. This review summarizes the recent research progress of TRIP13 and discusses the potential of targeting TRIP13 to improve immune-based therapies for patients with cancer.
如何引用
Jing S, Zhao L, Zhao L, Gao Y-J, He T. TRIP13: a promising cancer immunotherapy target. Cancer Innov. 2024; 3:e147.
https://doi.org/10.1002/cai2.147
02
标题
Impact of metallic nanoparticles on gut microbiota modulation in colorectal cancer: A review
金属纳米颗粒对结直肠癌肠道菌群调节的影响
作者
Akash Kumar, Jhilam Pramanik, Kajol Batta, Pooja Bamal, Mukesh Gaur, Sarvesh Rustagi, Bhupendra G. Prajapati*, Sankha Bhattacharya*
图片摘要
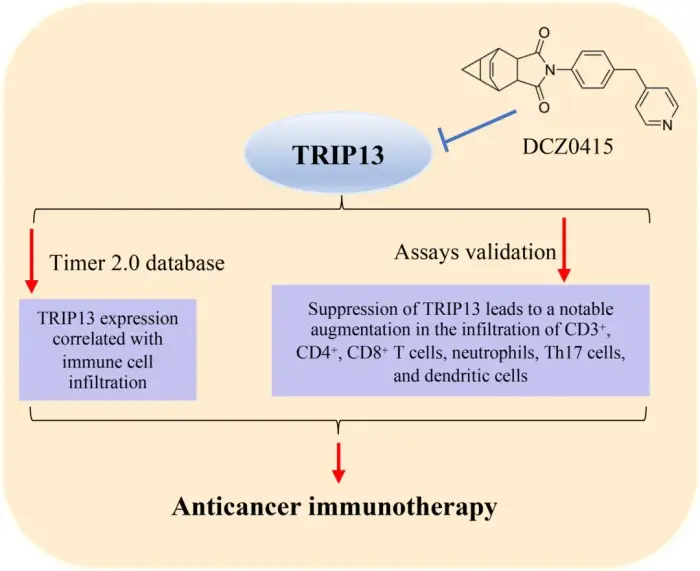
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the third most prevalent cancer. Ongoing research aims to uncover the causes of CRC, with a growing focus on the role of gut microbiota (GM) in carcinogenesis. The GM influences CRC development, progression, treatment efficacy, and therapeutic toxicities. For example, Fusobacterium nucleatum and Escherichia coli can regulate microbial gene expression through the incorporation of human small noncode RNA and potentially contribute to cancer progression. Metallic nanoparticles (MNPs) have both negative and positive impacts on GM, depending on their type. Several studies state that titanium dioxide may increase the diversity, richness, and abundance of probiotics bacteria, whereas other studies demonstrate dose-dependent GM dysbiosis. The MNPs offer cytotoxicity through the modulation of MAPK signaling pathways, NF-kB signaling pathways, PI3K/Akt signaling pathways, extrinsic signaling pathways, intrinsic apoptosis, and cell cycle arrest at G1, G2, or M phase. MNPs enhance drug delivery, enable targeted therapy, and may restore GM. However, there is a need to conduct well-designed clinical trials to assess the toxicity, safety, and effectiveness of MNPs-based CRC therapies.
如何引用
Kumar A, Pramanik J, Batta K, Bamal P, Gaur M, Rustagi S, et al. Impact of metallic nanoparticles on gut microbiota modulation in colorectal cancer: a review. Cancer Innov. 2024; 3:e150. https://doi.org/10.1002/cai2.150
03
标题
Leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor B4: A keystone in immune modulation and therapeutic target in cancer and beyond
白细胞免疫球蛋白样受体B4:肿瘤及其他疾病免疫调节的关键和治疗靶点
作者
Qi Liu, Yuyang Liu, Zhanyu Yang*
图片摘要
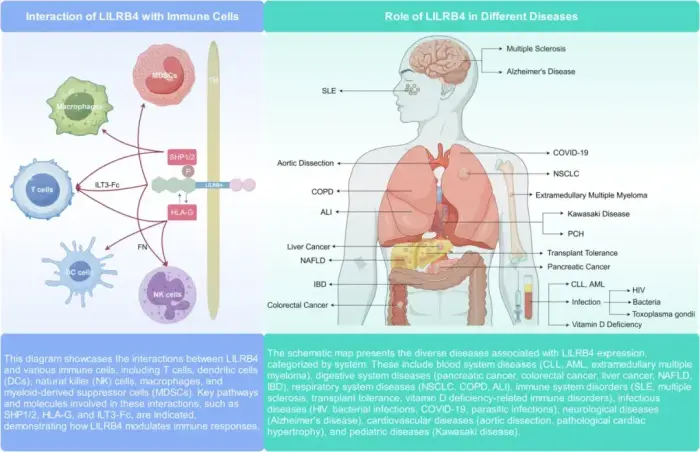
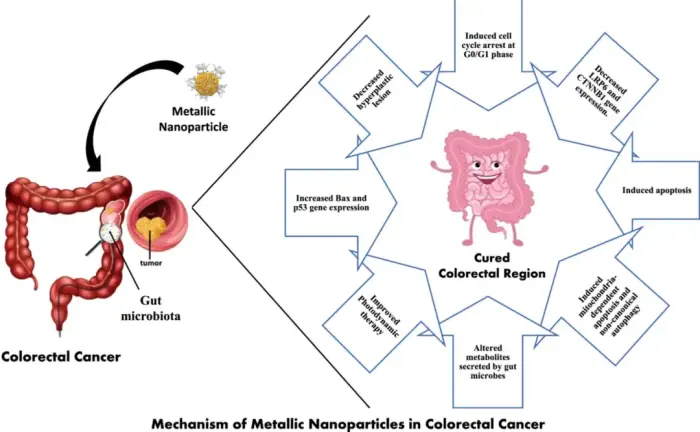
Leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor B4 (LILRB4) significantly impacts immune regulation and the pathogenesis and progression of various cancers. This review discusses LILRB4's structural attributes, expression patterns in immune cells, and molecular mechanisms in modulating immune responses. We describe the influence of LILRB4 on T cells, dendritic cells, NK cells, and macrophages, and its dual role in stimulating and suppressing immune activities. The review discusses the current research on LILRB4's involvement in acute myeloid leukemia, chronic lymphocytic leukemia, and solid tumors, such as colorectal cancer, pancreatic cancer, non-small cell lung cancer, hepatocellular carcinoma, and extramedullary multiple myeloma. The review also describes LILRB4's role in autoimmune disorders, infectious diseases, and other conditions. We evaluate the recent advancements in targeting LILRB4 using monoclonal antibodies and peptide inhibitors and their therapeutic potential in cancer treatment. Together, these studies underscore the need for further research on LILRB4's interactions in the tumor microenvironment and highlight its importance as a therapeutic target in oncology and for future clinical innovations.
如何引用
Liu Q, Liu Y, Yang Z. Leukocyte immunoglobulin-like receptor B4: a keystone in immune modulation and therapeutic target in cancer and beyond. Cancer Innov. 2024; 3:e153.
https://doi.org/10.1002/cai2.153
COMMENTARY
04
标题
Retinoic acid receptor responder 2 and lipid metabolic reprogramming: A new insight into brain metastasis
视黄酸受体应答基因2和脂质代谢重编程:脑转移的新见解
作者
Lulu Wang, Yan Gao*
图片摘要
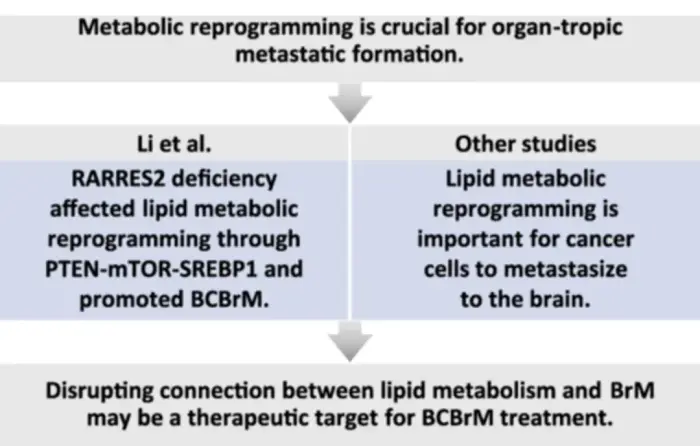
The brain is a common metastatic site for carcinoma, and metabolic reprogramming is crucial for organ-tropic metastatic formation. Li et al. found RARRES2 deficiency affected lipid metabolic reprogramming through PTEN-mTOR-SREBP1 pathway and promoted BCBrM. Other studies revealed that lipid metabolic reprogramming is part of metabolic adaptation to central nervous system. Overall, there is an intricate connection between lipid metabolism and brain metastases, and disrupting this connection may be a potential therapeutic target for BCBrM treatment.
如何引用
Wang L, Gao Y. Retinoic acid receptor responder 2 and lipid metabolic reprogramming: a new insight into brain metastasis. Cancer Innov. 2024; 3:e148. https://doi.org/10.1002/cai2.148
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
05
标题
Development and validation of the NCC-BC-A scale to assess patient-reported outcomes for breast cancer patients in China
中国乳腺癌患者报告结局量表(NCC-BC-A)的研发
作者
Fei Ma*, Xiaoyan Yan, Xiuwen Guan, Tianmou Liu, PRO-BC China Standards Committee
图片摘要
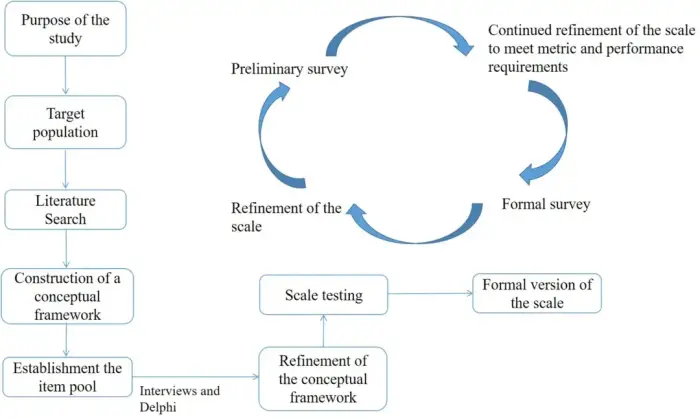
Background
The commonly used international patient-reported outcome scales for breast cancer were developed before the advent of multiple targeted therapies and immunotherapies, rendering them potentially insufficient for current clinical practices. Therefore, it is necessary to develop a specific patient-reported outcome scale tailored for breast cancer patients in China to optimize the management model for these patients.
Methods
A comprehensive literature search was performed in the PubMed, Embase, Wanfang, and CNKI databases to extract dimensions and items for a potential patient-reported outcome scale. The Delphi method was used to modify, add, subtract, and adjust the language of items until the experts reached a consensus on the first draft. This draft was further refined using a cognitive test and a presurvey. The optimized scale was used for a formal survey, and the items were further analyzed and screened using metrics such as the coefficient of variation, correlation coefficient, internal item consistency, factor analysis, reliability, and validity.
Results
A total of 10,954 articles were analyzed, and 237 were used to create a pool of 277 patient-reported outcome items. Through two rounds of Delphi expert consultation, the experts' authority coefficients were 0.739 and 0.826. After a cognitive test, several items were adjusted to enhance understanding. Further adjustments were made following a presurvey of 200 advanced breast cancer patients, resulting in a 38-item patient-reported outcomes scale, termed NCC-BC-A. In the national formal survey, 588 advanced breast cancer patients participated. Principal component analysis showed good consistency among the items and sufficient difference between the dimensions. The results were normally distributed with good variation. The Cronbach's α coefficient of the scale was 0.925 and the test–retest reliability was 0.9041.
Conclusion
The NCC-BC-A scale has high validity and reliability. It comprehensively considered the characteristics of systemic treatment for breast cancer, and the specific context within China. Its implementation may help clinicians to pay more attention to quality of life of breast cancer patients and to optimize the system for managing this condition.
如何引用
Ma F, Yan X, Guan X, Liu T, PRO-BC China Standards Committee. Development and validation of the NCC-BC-A scale to assess patient-reported outcomes for breast cancer patients in China. Cancer Innov. 2024; 3:e141. https://doi.org/10.1002/cai2.141
06
标题
Beyond clinical trials: CDK4/6 inhibitor efficacy predictors and nomogram model from real-world evidence in metastatic breast cancer
临床试验之外:CDK4/6抑制剂疗效预测因子和来自转移性乳腺癌真实世界证据的Nomogram模型
作者
Binliang Liu, Zhe-Yu Hu, Ning Xie, Liping Liu, Jing Li, Xiaohong Yang, Huawu Xiao, Xuran Zhao, Can Tian, Hui Wu, Jun Lu, Jianxiang Gao, Xuming Hu, Min Cao, Zhengrong Shui, Yu Tang, Quchang Ouyang*
图片摘要
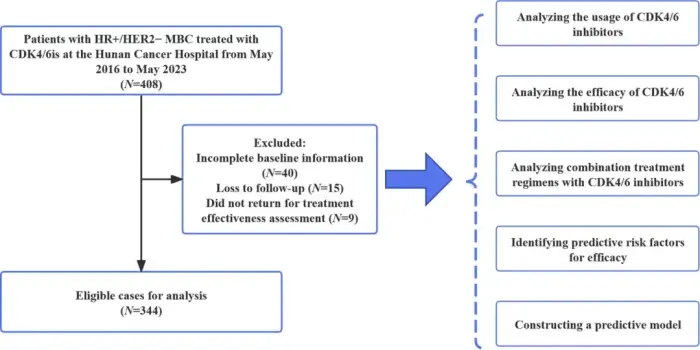
Background
CDK4/6 inhibitors (CDK4/6i) have shown promising results in the treatment of hormone receptor-positive (HR+) metastatic breast cancer (MBC) when combined with endocrine therapy (ET). It is crucial to evaluate the actual effectiveness and safety of CDK4/6i in clinical practice, as well as to analyze the factors that can predict their outcomes.
Methods
Patients with HR+ MBC who received CDK4/6i-based therapy between May 2016 and May 2023 at Hunan Cancer Hospital were evaluated for progression-free survival (PFS). Adverse reactions were assessed based on the National Cancer Institute Common Toxicity Criteria (version 5.0).
Results
This study included 344 patients, with a median PFS (mPFS) of 12.8 months (range: 10.4–15.2 months). After adjustment, Cox multivariate regression analysis revealed that visceral metastasis (specifically liver and brain metastases), Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Performance Status (ECOG PS) ≥ 1, estrogen receptor ≤ 80%, progesterone receptor ≤ 10%, Ki-67 > 30%, and treatment in later stages were significant factors associated with reduced PFS. Based on this, we created a prognostic nomogram and validated its performance, obtaining a C-index of 0.714 (95% confidence interval: 0.640–0.787) as well as reliable calibration and clinical impact. The mPFS of CDK4/6i rechallenge was 7.7 months; for patients who initially discontinued CDK4/6i for reasons other than disease progression, CDK4/6i rechallenge still provided a mPFS of 11.4 months. The tolerability and safety of combining CDK4/6is with ET were manageable. Adverse events led to treatment discontinuation in 3.8% of patients. Neutropenia (29.1%), leukopenia (13.7%), and anemia (4.1%) were the primary grade 3/4 adverse reactions.
Conclusions
This real-world study highlights the ample efficacy and reasonable safety of combined CDK4/6i and ET in patients with HR+ MBC. Individualized treatment decisions and ongoing safety monitoring are important to optimize the therapeutic benefit of CDK4/6i treatment.
如何引用
Liu B, Hu Z-Y, Xie N, Liu L, Li J, Yang X, et al. Beyond clinical trials: CDK4/6 inhibitor efficacy predictors inhibitor efficacy predictors and nomogram model from real-world evidence in metastatic breast cancer.Cancer Innov. 2024; 3:e143. https://doi.org/10.1002/cai2.143
07
标题
Combination therapy using low-dose anlotinib and immune checkpoint inhibitors for extensive-stage small cell lung cancer
低剂量安罗替尼和免疫检查点抑制剂联合治疗广泛期小细胞肺癌研究
作者
Han Li, Shumin Yuan, Han Wu, Yajie Wang, Yichen Ma, Xiance Tang, Xiaomin Fu, Lingdi Zhao, Benling Xu, Tiepeng Li, Peng Qin, Hongqin You, Lu Han, Zibing Wang*
图片摘要
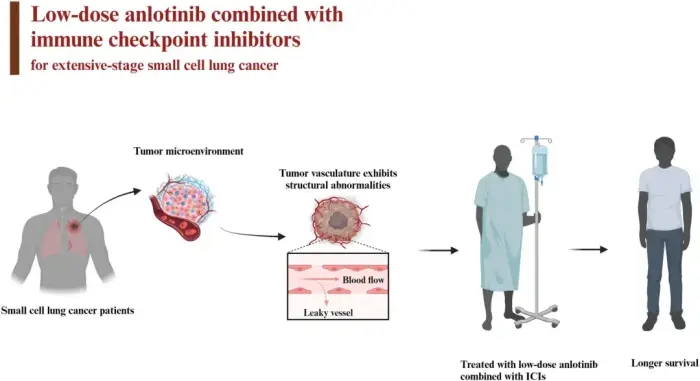
Background
This study evaluated the efficacy and safety of low-dose anlotinib combined with immune checkpoint inhibitors as second-line or later treatment for extensive-stage small cell lung cancer (ES-SCLC).
Methods
The study included 42 patients with ES-SCLC who were treated with low-dose anlotinib combined with programmed cell death protein 1/programmed cell death-ligand 1 inhibitors at Henan Cancer Hospital between March 2019 and August 2022. We retrospectively analyzed the efficacy and safety data for these patients. Indicators assessed included progression-free survival (PFS), overall survival (OS), the overall response rate (ORR), the disease control rate (DCR), and adverse events (AEs). Prognostic factors were identified in univariate and multivariate analyses.
Results
Median PFS was 11.0 months (95% CI: 7.868–14.132) and median OS was 17.3 months (95% CI: 11.517–23.083). The ORR was 28.5% and the DCR was 95.2%. Treatment-related AEs were noted in 27 patients (64.3%), the most common of which was thyroid dysfunction (26.2%). Grade 3/4 treatment-related AEs were observed in two patients (4.8%).
Conclusions
A combination of low-dose anlotinib and immune checkpoint inhibitors as second-line or later treatment for ES-SCLC may achieve longer PFS and OS and have manageable AEs.
如何引用
Li H, Yuan S, Wu H, Wang Y, Ma Y, Tang X, et al. Combination therapy using low-dose anlotinib and immune checkpoint inhibitors for extensive-stage small cell lung cancer. Cancer Innov. 2024; 3:e155.
https://doi.org/10.1002/cai2.155
08
标题
Prognostic nomograms for young breast cancer: A retrospective study based on the SEER and METABRIC databases
年轻乳腺癌患者的预后图谱:基于SEER和METABRIC数据库的回顾性研究
作者
Yongxin Li, Xinlong Tao, Yinyin Ye, Yuyao Tang, Zhengbo Xu, Yaming Tian, Zhen Liu*, Jiuda Zhao*
图片摘要
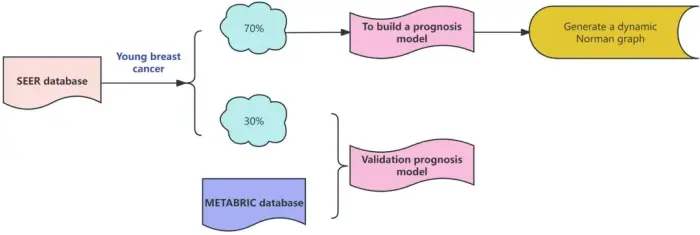
Background
Young breast cancer (YBC) is a subset of breast cancer that is often more aggressive, but less is known about its prognosis. In this study, we aimed to generate nomograms to predict the overall survival (OS) and breast cancer-specific survival (BCSS) of YBC patients.
Methods
Data of women diagnosed with YBC between 2010 and 2020 were obtained from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) database. The patients were randomly allocated into a training cohort (n = 15,227) and internal validation cohort (n = 6,526) at a 7:3 ratio. With the Cox regression models, significant prognostic factors were identified and used to construct 3-, 5-, and 10-year nomograms of OS and BCSS. Data from the Molecular Taxonomy of Breast Cancer International Consortium (METABRIC) database were used as an external validation cohort (n = 90).
Results
We constructed nomograms incorporating 10 prognostic factors for OS and BCSS. These nomograms demonstrated strong predictive accuracy for OS and BCSS in the training cohort, with C-indexes of 0.806 and 0.813, respectively. The calibration curves verified that the nomograms have good prediction accuracy. Decision curve analysis demonstrated their practical clinical value for predicting YBC patient survival rates. Additionally, we provided dynamic nomograms to improve the operability of the results. The risk stratification ability assessment also showed that the OS and BCSS rates of the low-risk group were significantly better than those of the high-risk group.
Conclusions
Here, we generated and validated more comprehensive and accurate OS and BCSS nomograms than models previously developed for YBC. These nomograms can help clinicians evaluate patient prognosis and make clinical decisions.
如何引用
Li Y, Tao X, Ye Y, Tang Y, Xu Z, Tian Y, et al. Prognostic nomograms for young breast cancer: a retrospective study based on the SEER and METABRIC databases. Cancer Innov. 2024; 3:e152. https://doi.org/10.1002/cai2.152
